Wi-Fi & LTE Antenna Installations: How To Choose the Best Coaxial Cable
Choosing the best antenna cable coax for an outdoor Wi-Fi antenna installation involves considering several factors to ensure good signal quality, overall performance, and durability.
Use one of these high-quality, double-shielded coaxial cable types:
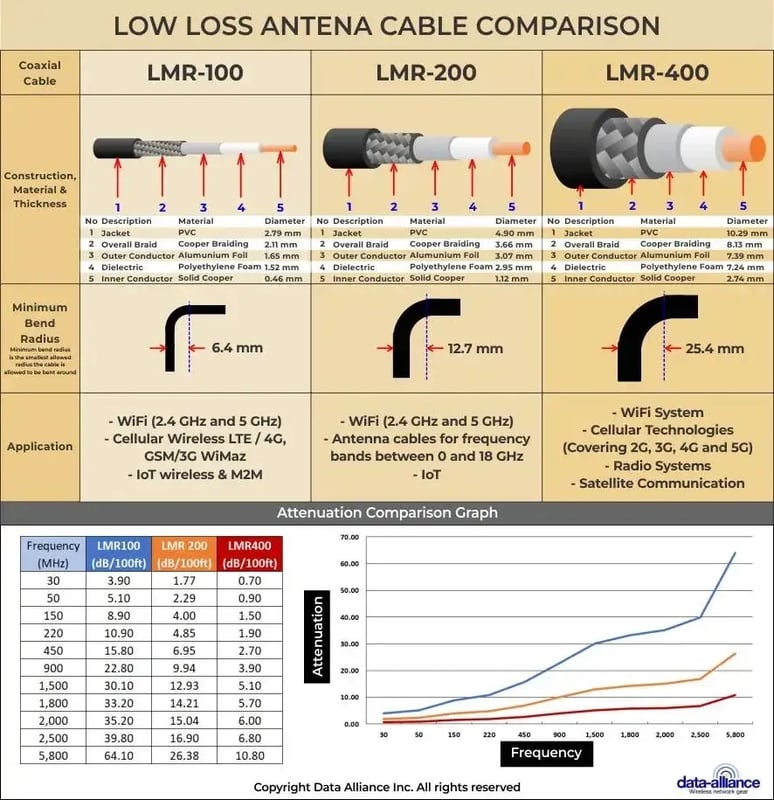
- For longer cable runs: Use LMR-400 or equivalent, to minimize signal loss.
- For cable runs of two feet up to six feet: Depending on your need for cost-efficiency diameter and bend radius: You can use LMR-400, LMR-200, or LMR-100.
- For cable runs: You should use LMR-200 or LMR-400, for lower signal loss (attenuation). You can use LMR-100 up to as long as 12 feet, but it's better to use LMR-200 or 400.
- For longer cable runs, over 20 feet: You can use LMR-200, but you should more seriously consider LMR-400 due to its low loss characteristics at Wi-Fi frequencies.
Other considerations to help you make an informed decision:
- Impedance: Ensure the cable impedance matches your system requirements. Wi-Fi and LTE equipment use 50-ohm cable. LMR-100, LMR-200, and LMR-400 all are compatible 50-ohm coaxial cable types, Using the wrong impedance can lead to signal loss and reduced performance.
- Shielding: Good cable shielding is important to protect against interference from other electronic devices and signals, especially in crowded urban environments. Look for a cable with multiple layers of shielding, such as a combination of foil and braided metal. LMR-100, 200 and 400 are double-shielded, and thus offer better interference rejection than single-shielded RG-series cables.
- Attenuation: Attenuation refers to signal loss over the length of the cable. It's important to choose a cable with low attenuation, especially for long runs. The cable's datasheet should list attenuation values at different frequencies, allowing you to choose a cable that minimizes loss at Wi-Fi frequencies (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz). The various coax types have have different amounts of signal loss per foot (or meter), that varies based on the shielding and the diameter of the conductor wire. Check the specifications for attenuation, which is usually given in dB per 100 feet. Lower is better.
- Cable Length: Use the shortest length of cable possible to connect your antenna to your device. Longer cables result in more signal loss (attenuation). In some cases, you might need to extend the reach of an existing cable connection. In such scenarios, you can use an SMA extension cable. These cables maintain the same connector type (SMA) on both ends and allow you to add additional length to your existing cable run while minimizing signal loss. In such a situation, you can use antenna cable adapters to switch between different connectors.
- Weather Resistance: Since the installation is outdoors, the cable must be able to withstand environmental conditions such as UV exposure, rain, and temperature fluctuations. Look for cables with UV-resistant jackets and waterproofing features. Weatherproofing for cables and connectors for outdoor use, and a durable outer jacket are important features, especially for installations that will be exposed to the elements.
- Flexibility and Durability: Consider the installation environment and whether the cable needs to be routed through tight spaces or around sharp corners. Some cables are more flexible, but this can sometimes come at the cost of durability and shielding effectiveness.
- Connector Compatibility: Ensure the cable is compatible with the connectors used by your antenna and Wi-Fi equipment. The most common connectors for outdoor Wi-Fi antennas are N-Type. SMA cables can also be used in certain situations. They offer a good balance between performance and cost compared to LMR cables and might be suitable for specific applications where N-Type connectors are not compatible. RP-SMA is more common for indoor antennas.. The quality of the connectors and the installation (properly crimped and weatherproofed) are crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
- Use Quality Connectors: Poor-quality connectors can introduce noise and signal loss. Use high-quality, corrosion-resistant connectors and ensure they are properly attached. Nickel-plated Type-N connectors are the superior option for outdoor installations.
- Length: Minimize the cable length to reduce signal loss, but ensure it's long enough to reach from your Wi-Fi device to the antenna without stretching or creating sharp bends.
- Shielding: Double or triple-shielded cables can offer better protection.
- Cost: While it's important to choose a high-quality cable to ensure the best performance of your Wi-Fi antenna, consider your budget. More expensive cables offer better performance but evaluate if the cost is justified for your specific needs.
- Brand and Quality: Choose cables from reputable manufacturers to ensure quality and reliability. It's also beneficial to read reviews and seek recommendations from professionals or forums where similar installations are discussed.
- Frequency Range: Ensure the cable can handle the frequency range required for your application. LMR-100, LMR-200 and LMR-400 all are compatible with the Wi-Fi and LTE frequency bands.
Remember, the best cable for your installation depends on your specific needs, the distance between your antenna and your wireless device, the type of signals you're receiving (e.g., Wi-Fi, LTE, GPS), and the environment in which the cable will be installed.
Posted by George Hardesty on 17th Feb 2024

























