Antennas, Antenna Cables, Wireless Products: Technical Articles
WiFi Channels: Complete Guide with Tips to Boost Signal Performance
Table of Contents
WiFi Channels: Complete Guide to 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and Channel Planning
WiFi performance depends on more than just your internet speed. One of the most overlooked factors affecting speed, stability, and reliability is WiFi channel selection. Proper channel planning reduces interference, improves throughput, and delivers a better overall WiFi experience—especially in crowded residential, office, and IoT environments.
This guide explains how WiFi channels work, how interference occurs, and how to select the best WiFi channels for optimal performance.
WiFi speed and reliability depend heavily on channel selection and interference management, especially in crowded environments.
Key Topics Covered in This Guide
- Channel planning will help you get the best WiFi connection.
- Using non-overlapping channels can boost WiFi network performance.
- What are the best WiFi channels?
- How can I change WiFi channels?
WiFi Channels by Frequency Band
WiFi channels: 2.4 GHz
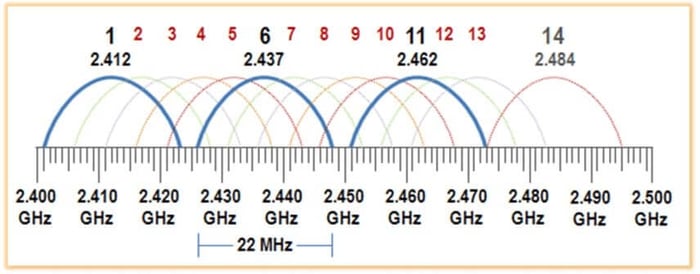
There are fourteen 20MHz wide channels in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. In North America, only 11 channels, numbered 1 to 11, are legally available in the United States. The use of the channels above 11 is usually restricted by firmware.
To utilize the approximately 100 MHz of available spectrum, these WiFi channels must overlap. Only channels 1, 6, and 11 have non-overlapping frequency space.
The 2.4 GHz band is widely used because of its longer range and better wall penetration, but it is also the most congested WiFi band. Careful channel selection is critical to reduce interference and maintain stable performance.
Channel number and frequency range (MHz):
| Channel number | Frequency range (MHz) |
| 1 | 2401 - 2423 |
| 2 | 2406 - 2428 |
| 3 | 2411 - 2433 |
| 4 | 2416 - 2438 |
| 5 | 2421 - 2443 |
| 6 | 2426 - 2448 |
| 7 | 2431 - 2453 |
| 8 | 2436 - 2458 |
| 9 | 2441 - 2463 |
| 10 | 2446 - 2468 |
| 11 | 2451 - 2473 |
WiFi channels: 5 GHz
There are 25 available channels in the 5 GHz WiFi band, and they are all non-overlapping. Due to the greater amount of available spectrum, channels can be combined into 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and 160 MHz-wide channels, enabling much higher data rates than 2.4 GHz.
The 5 GHz band offers lower interference, higher throughput, and better performance for streaming, gaming, and business networks. Some channels support Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS), which allows routers to automatically change channels to avoid radar interference.
Channel number and frequency range (MHz):
| Channel number | Frequency Range (MHz) | |
| U-NII 1 | 36 | 5170–5190 |
| 40 | 5190–5210 | |
| 44 | 5210–5230 | |
| 48 | 5230–5250 | |
| U-NII 2a | 52 | 5250–5270 |
| 56 | 5270–5290 | |
| 60 | 5290–5310 | |
| 64 | 5310–5330 | |
| U-NII 2c | 100 | 5490–5510 |
| 104 | 5510–5530 | |
| 108 | 5530–5550 | |
| 112 | 5550–5570 | |
| 116 | 5570–5590 | |
| 120 | 5590–5610 | |
| 124 | 5610–5630 | |
| 128 | 5630–5650 | |
| 132 | 5650–5670 | |
| 136 | 5670–5690 | |
| 140 | 5690–5710 | |
| 144 | 5710–5730 | |
| U-NII 3 | 149 | 5735–5755 |
| 153 | 5755–5775 | |
| 157 | 5775–5795 | |
| 161 | 5795–5815 | |
| 165 | 5815–5835 |
WiFi Channels: 6 GHz (WiFi 6E & WiFi 7)
Newer WiFi standards such as WiFi 6E and WiFi 7 extend operation into the 6 GHz band. This band provides a large amount of clean, uncongested spectrum and supports many non-overlapping channels.
Key advantages of 6 GHz WiFi include:
- No legacy device interference
- Lower latency
- Higher throughput
- Excellent performance in dense environments
Availability and channel counts vary by country and regulatory region, but 6 GHz represents the cleanest WiFi spectrum available today.
It can be easy to overlook the distribution of channels used for WiFi networking but channel planning makes all the difference to boosting the quality and utility of your WiFi connection.
Channel Overlap and Interference
It can be easy to overlook the distribution of channels used for WiFi networking, but channel planning makes all the difference in boosting connection quality and reliability.
Overlapping WiFi channels can cause interference, resulting in slow or inconsistent connectivity. Although overlapping channels may operate acceptably under light load, heavy usage and high throughput increase the likelihood of performance degradation.
Adjacent Channel Interference (ACI)
Adjacent channel interference occurs when access points or devices operate on overlapping channels. Devices must wait for the channel to clear before transmitting, which reduces efficiency and throughput. At 2.4 GHz, channels 2 through 5 and 7 through 10 are most affected by ACI.
Co-Channel Interference (CCI)
Co-channel interference occurs when two or more access points use the same channel. This blends their coverage areas and forces devices to share airtime, significantly reducing performance. Devices must wait for all other devices on the same channel—across multiple access points—before transmitting.
Why Non-Overlapping Channels Matter
Using non-overlapping channels can significantly boost WiFi network performance.
Channel planning involves spacing WiFi channels to reduce interference. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the only non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz band and can be used without sharing frequency space.
When multiple access points are deployed, a three-channel plan using channels 1, 6, and 11 helps avoid channel sharing and co-channel interference. Spacing channels with a three-to-four-channel gap further reduces interference.
What Are the Best WiFi Channels?
Best WiFi Channels for 2.4 GHz
Non-overlapping channels 1, 6, and 11 are considered the best WiFi channels at 2.4 GHz.
Channels 1 and 11 do not overlap with other channels and are generally best for avoiding interference.
Channel 6 is also non-overlapping, but many routers default to channel 6, making it the most congested in many areas.
If you do not use channel 1 or 11, neighboring networks may overlap and disrupt your WiFi traffic.
Best WiFi Channels for 5 GHz
At 5 GHz, you have 23 non-overlapping channels, making congestion far less likely. Routers with DFS capability can automatically select cleaner channels to minimize interference.
Using wider channel widths (40 MHz instead of 20 MHz) can increase throughput when interference levels are low. Common 40 MHz channel groupings include:
36–40
44–48
149–153
157–161
While channel recommendations provide a strong starting point, real-world performance depends on local congestion. WiFi analyzers can help identify underutilized channels, and automatic channel selection can be effective in dynamic environments.
Hardware Considerations: Antennas and Cables
Selecting the best WiFi channel is only part of achieving optimal performance. Antenna selection, antenna gain, cable quality, and connector compatibility (such as SMA vs RP-SMA) all influence signal strength and coverage.
Higher frequencies such as 5 GHz and 6 GHz are more sensitive to antenna quality and cable loss. Using properly matched antennas and low-loss cables can significantly improve range, reliability, and throughput—especially for IoT, outdoor, and long-cable-run installations.
What Are WiFi Channels?
WiFi channels are non-overlapping sub-bands within the main frequency bands used for wireless communication. Each frequency band supports a specific number of channels that routers and devices use to exchange data.
Channels typically have 5 MHz spacing, with wider spacing at higher frequencies where more spectrum is available. Channel availability and spacing vary by region and regulatory domain. Some WiFi standards allow channels to be bonded together to increase throughput.
Although channels may be non-overlapping, WiFi uses contention-based access. When multiple devices share a channel, available bandwidth and airtime are divided among them.
How Can I Change WiFi Channels?
WiFi channel selection is configured at the router. Many routers default to channel 6 on the 2.4 GHz band.
To change your WiFi channel:
- Log in to your router’s web-based interface
- Navigate to wireless settings
- Select the frequency band (2.4 or 5 GHz)
- Choose a specific channel or enable automatic selection
- Save settings and reboot if required
Using a WiFi scanner can help identify congested channels before making changes.
Conclusion
Choosing the right WiFi channel is one of the simplest and most effective ways to improve wireless performance. By understanding how channels work across the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands—and by avoiding overlapping and congested channels—you can significantly reduce interference and increase speed, reliability, and overall network quality. Combined with proper channel planning, appropriate channel widths, and quality antennas and cabling, thoughtful WiFi channel selection helps ensure consistent performance in residential, business, and IoT environments.
MORE INFO:
- Top WiFi Tips for improving your signal strength, speed, and network performance.
- Detailed explanation of all WiFi types (WiFi network standards) with advantages and disadvantages of each and frequency bands used.
FAQs
What are the best WiFi channels for 2.4 GHz networks?
The best WiFi channels for 2.4 GHz are channels 1, 6, and 11 because they do not overlap with each other. Using these channels helps reduce interference and improves network stability, especially in crowded environments.
Why is the 2.4 GHz WiFi band more congested than 5 GHz?
The 2.4 GHz band has fewer available channels and is used by many devices, including Bluetooth, cordless phones, and IoT equipment. This heavy usage increases interference, making careful channel selection essential.
What are DFS channels in the 5 GHz WiFi band?
DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) channels are 5 GHz channels that monitor for radar signals. If radar is detected, the router automatically switches channels to avoid interference. DFS channels are often less congested and can provide better performance.
Is 5 GHz WiFi always better than 2.4 GHz?
Not always. While 5 GHz offers higher speeds and less interference, it has shorter range and weaker wall penetration than 2.4 GHz. The best choice depends on distance, obstacles, and device capabilities.
What makes 6 GHz WiFi (WiFi 6E and WiFi 7) different?
The 6 GHz band provides a large amount of clean, uncongested spectrum with no legacy devices. This results in lower latency, higher throughput, and improved performance in dense environments, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
How does WiFi channel width affect performance?
Wider channel widths (such as 40, 80, or 160 MHz) allow higher data rates but are more sensitive to interference. In congested environments, narrower channels often deliver more consistent real-world performance.
How often should I change my WiFi channel?
You should review and adjust your WiFi channel if you experience slow speeds, frequent dropouts, or add new devices nearby. Periodic scans with a WiFi analyzer can help identify less congested channels and improve performance.







