Antennas, Antenna Cables, Wireless Products: Technical Articles
RSSI & Antenna Performance and IoT Wireless Applications
Table of Contents
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is a measurement of the power level of a received radio signal
- Key Points about RSSI:
- Examples of Usage
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) plays a critical role in the performance of antennas and IoT wireless applications
- RSSI & IoT Wireless Applications
- RSSI Optimization for IoT Antennas
- Example Use Cases in IoT Wireless Antenna Systems
- Signal Optimization Through Software Configuration
- Hardware Enhancements
- Monitoring & Feedback Loop
- Conclusion
- FAQs
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is a measurement of the power level of a received radio signal
RSSI is commonly used in wireless communication systems such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks, and other RF-based technologies to determine the strength of the signal being received by a device.
Key Points about RSSI:
- Measurement Unit: Usually expressed in dBm (decibel-milliwatts), though sometimes it is presented as a raw value (e.g., 0 to 255) depending on the hardware or software used.
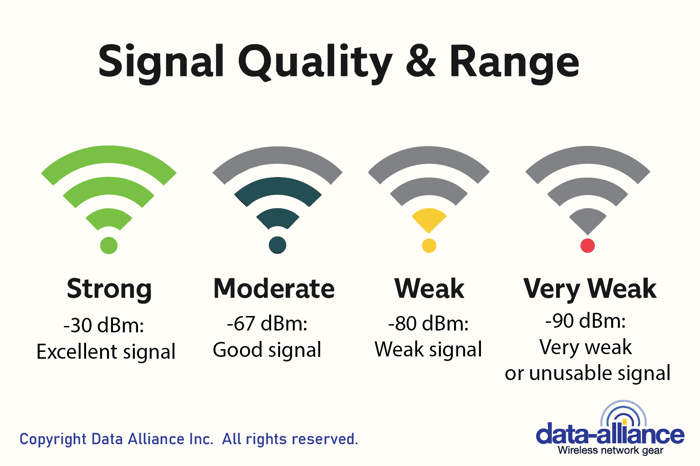
- Scale: Typically a negative number in dBm; closer to 0 means a stronger signal. For example:
- -30 dBm: Excellent signal (very strong)
- -67 dBm: Good signal (acceptable for most applications)
- -80 dBm: Weak signal (might work but could be unstable)
- -90 dBm: Very weak or unusable signal
- Purpose: Helps determine the quality of the connection, range, and stability. A higher RSSI value (closer to 0) generally indicates a better quality of signal.
- Application: Used for site surveys, troubleshooting, and optimizing wireless networks.
Examples of Usage
- Wi-Fi Networking: RSSI is used to assess the strength of a Wi-Fi signal at various points within a building to optimize router placement.
- Bluetooth Communication: Devices use RSSI to estimate the proximity of other devices (e.g., Bluetooth beacons).
- Cellular Networks: Helps in handoff decisions between cells and determining network quality.
Would you like me to explain how RSSI relates to antennas and IoT wireless applications?
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) plays a critical role in the performance of antennas and IoT wireless applications
RSSI & Antennas
FAQs
What is RSSI and why is it important?
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power of a received radio signal, helping assess connection quality, range, and network stability in wireless systems.
How is RSSI measured?
RSSI is usually expressed in dBm (decibel-milliwatts), often as a negative number. Some devices may report it as raw values (e.g., 0–255), depending on hardware or software.
What RSSI values indicate good or bad signal strength?
- -30 dBm: Excellent (very strong)
- -67 dBm: Good (works for most uses)
- -80 dBm: Weak (may be unstable)
- -90 dBm: Very weak or unusable
How does RSSI relate to antennas?
RSSI reflects how effectively an antenna receives a signal. Antenna gain, type (directional vs. omnidirectional), and positioning all directly influence RSSI.
How is RSSI used in IoT applications?
In IoT systems, RSSI helps monitor connectivity, optimize antenna placement, improve power efficiency, map coverage areas, and guide mesh network routing.
What tools can be used to measure RSSI?
RSSI can be measured using built-in device commands (e.g., Wi-Fi iwconfig, LoRa AT+RSSI?), software analyzers (Wireshark, NetSpot, nRF Connect), or specialized RF tools like spectrum analyzers and signal meters.
How can RSSI be improved?
Improving RSSI involves optimizing antenna selection, placement, and orientation, reducing interference, adjusting transmission power, and in some cases using amplifiers, high-quality cables, or antenna arrays.
Why is RSSI critical for IoT devices and wireless networks?
Because IoT devices often operate in interference-prone environments, monitoring and optimizing RSSI ensures reliable communication, efficient power use, and broader coverage.