Mounts for Antennas & Gear
Mounting Brackets, Bases, Stands for Small and Large Antennas
Antennas are crucial components in a wide array of communication systems. However, the efficacy of an antenna doesn't just rely on its design or frequency compatibility; its placement and orientation play a pivotal role too. This is where antenna mounts come into play. These specialized fixtures offer secure mounting solutions, ensuring optimal signal reception and transmission. Let's delve into the different types of antenna mounts, their key features, and applications.
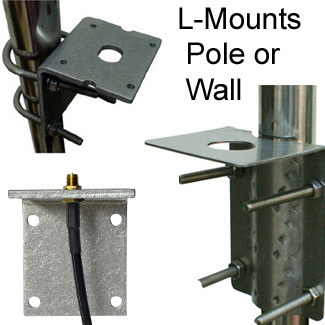
1. L-Bracket Mounts
Key Features:
- L-mounts and U-bolts are used together to make a pole mount, or the L-bracket mount is attached directly to a wall.
- U-bolts are U-shaped bolts with threading on either side. They are used as part of another type of mount, to clamp brackets on mounts such as L-mounts and to clamp antennas onto masts. Their sizes vary for use on different masts, they can also be right-angled to clamp square pipes.
Applications:
-
- Small antennas for Internet of Things
2. Pole Mounts
Key Features:
- Pole mounts usually incorporate L-mounts and U-bolts and sometimes a mast. Some antennas require special brackets for pole mounting. The mounting point has adjustable height, pitch, and direction. Pole mounts are favored for mounting sectoral antennas.
- Stability: Generally used with larger antennas, these mounts provide a sturdy base.
- Height Adjustment: Many mast mounts come with telescopic features, allowing height adjustments for optimal signal reception.
- Durable Materials: Often made from materials like galvanized steel or aluminum to resist environmental challenges.
Applications:
- Broadcast antennas for radio and television.
- Amateur radio setups.
- Weather monitoring stations.
3. Magnetic Mounts
Key Features:
- Magnetic mounts have a magnetic base to securely attach onto a magnetic surface such as a vehicle’s body. It is used for small lightweight RP-SMA / SMA omnidirectional antennas.
- Ease of Installation: Magnetic mounts can be easily affixed to metal surfaces without any tools.
- Portability: Ideal for temporary setups or for those on the move.
- Compact Design: Typically smaller, making them suitable for vehicles.
Applications:
- Car antennas for mobile radio or cellular boosters.
- Portable amateur radio setups.
- Temporary setups for events or mobile broadcast units.
4. Wall and Roof Mounts
Key Features:
- Wall mounting can be achieved by using J-poles, L-mounts, wall brackets or U-bolts. The J-pole, also called J-mount, is a curved or angled mast commonly used for wall mounts due to its adjustable features. Wall brackets may be specific to antenna.
- Space-saving: Ideal for locations with limited ground space.
- Variability: Can be used for both directional and omnidirectional antennas.
- Sturdy Installation: Often affixed using screws or brackets, ensuring a secure hold against weather conditions.
Applications:
- Satellite dish installations.
- Home TV antennas.
- Wireless network antennas in urban settings.
5. Tripod Mounts
Key Features:
- Tripods mounts are generally used for larger antennas such as parabolic, including for heavy satellite dish antennas. They have precise adjustments for dish orientation and a stable anchorage. Tripods can be placed on level ground or rooftops. Portability: Easy to fold and transport.
- Adjustability: Most tripod mounts offer angle adjustments.
- Quick Setup: Ideal for situations requiring rapid deployment.
Applications:
- Temporary communication setups, such as on construction sites or events.
- Field experiments and signal testing.
- Portable amateur radio operations.
6. Roof Mounts
There are three popular methods; Using non-penetrating mounts (which are held down by weights), bolted tripods, and J-mounts. Roof mounts are built with pitch and height adjustments. Data Alliance carries two tile roof mount options. Antenna specific roof mounts are also available. It is important to assess the load bearing ability of a roof before mounting heavy antennas on it, especially when using non-penetrating roof mounts.
7. Window and Glass Mounts
Key Features:
- Window mounts, used for small portable antennas for temporally mounting has a base with a rubber suction cup that can easily attach and detach from smooth surfaces such as windows and walls.
- Non-Intrusive: Designed to be discreet and non-damaging to surfaces.
- Ease of Installation: Often utilize suction cups or adhesives.
- Indoor Compatibility: Often used for indoor antennas or in situations where outdoor mounting isn't feasible.
Applications:
- Cellular signal boosters.
- Indoor radio or TV antennas.
- Temporary setups in rented properties.
8. Chimney Mounts
Key Features:
- Elevated Position: Provides a height advantage without needing a separate mast.
- Secure Strapping: Typically uses metal straps to wrap around the chimney securely.
- Non-permanent: Doesn't damage or alter the structure of the chimney.
Applications:
- Residential TV antennas.
- Amateur radio antennas in suburban settings.
- Weather measurement tools in homes.
Conclusion
Antenna mounts are as varied as the applications they support. They ensure that antennas remain secure, oriented correctly, and positioned optimally for the best signal reception and transmission. When selecting a mount, it's essential to consider the specific application, environment, and requirements at hand to ensure efficient and uninterrupted communication.